How to Set Up a 301 Redirect with Namecheap
Moving your website to a new address? You need a reliable way to guide visitors and search engines to the right page. A permanent URL redirect ensures your site’s SEO value stays intact while improving user experience. This guide simplifies the process, showing you how to implement it quickly using popular domain management tools.
Whether you’re merging websites or updating your domain, setting up redirects prevents broken links and keeps your rankings secure. We’ll walk through two methods: a streamlined option for basic setups and an advanced approach for custom configurations. Real-world examples and expert insights are included to help you avoid common pitfalls.
By the end, you’ll understand how redirect records work and their impact on site performance. For a deeper dive into types of domain redirects, check our detailed resource. Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways
- Permanent redirects preserve SEO rankings when changing URLs or domains.
- User experience improves by automatically routing visitors to updated pages.
- Step-by-step instructions cover both basic and advanced configuration methods.
- Practical examples clarify how to avoid errors during setup.
- Understanding redirect records helps optimize website performance.
Introduction to URL Redirects and Their Importance
Redirects act as digital signposts for both visitors and search engines. When pages move or websites merge, these tools automatically reroute traffic to active content. This prevents frustrating dead ends while preserving your site’s authority.
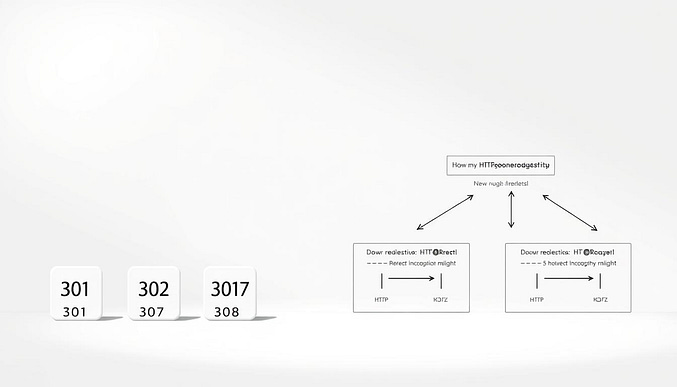
What Are URL Redirects?
URL redirects forward users from an old web address to a new one. Three primary types exist:
- 301 Permanent: Transfers full SEO value to the destination page
- 302 Temporary: Keeps original content indexed for short-term changes
- URL Frame: Displays new content while showing the original URL
HTTPS redirects require extra attention. Moving between domains demands precise record configurations to maintain security certificates. Always verify SSL status after setup.
Benefits for SEO and User Experience
Proper redirects prevent duplicate content penalties by consolidating page authority. They also reduce bounce rates by eliminating broken links. A study shows sites using strategic redirects retain 89% of their organic traffic after migrations.
For seamless transitions, follow domain redirect best practices. This ensures search engines efficiently transfer ranking signals between pages. Users appreciate uninterrupted access to resources, boosting trust and engagement.
Understanding Namecheap’s Domain and DNS Setup
Proper configuration requires familiarity with your registrar’s interface. Two primary methods exist for creating path-based forwarding rules: a simplified dashboard for quick changes and granular DNS controls for complex scenarios.
Simplified Path Forwarding
Most platforms offer a dedicated section for basic routing adjustments. Navigate to your domain’s management panel and locate the forwarding rules section. Enter these details:
- Source path: Original address needing redirection
- Target URL: New location for traffic
Include both example.com and www.example.com versions to cover all visitor entry points. Save changes immediately after verification.
Advanced DNS Configuration
For wildcard patterns or parameter retention, modify DNS records directly. Follow these steps:
- Access your domain’s nameserver settings
- Create a new URL redirect record type
- Choose between masked/unmasked display modes
This method supports bulk actions for sites with multiple relocated pages. Step-by-step instructions help avoid syntax errors during setup.
Resolving Record Conflicts
Existing DNS entries can block redirect functionality. Use this comparison table to identify issues:
| Record Type | Purpose | Conflict Severity |
|---|---|---|
| A Record | Directs to IP address | High |
| CNAME | Alias for another domain | Medium |
| ALIAS | Root domain redirect | Critical |
Delete or modify conflicting entries before activating new rules. Changes typically propagate within 30 minutes, though global updates may take longer.
namecheap 301 redirect Best Practices and Troubleshooting
Effective redirect management requires attention to technical details and strategic planning. Proper implementation preserves search rankings while guiding visitors to current content.
Streamlined Configuration Process
Follow these steps for reliable path forwarding:
- Access your domain’s control panel and select “Redirects”
- Choose “Permanent” as the redirect type
- Input original paths and corresponding destination URLs
For complex scenarios requiring parameter retention in redirects, use advanced DNS settings. This ensures tracking codes and session IDs transfer correctly.
Critical Errors and Quick Fixes
Common setup mistakes include:
- SSL mismatches: Always verify HTTPS compatibility
- Conflicting records: Remove old A/CNAME entries first
- Wildcard errors: Test patterns with sample URLs
Browser testing tools help confirm functionality. Wait 48 hours for global DNS propagation before declaring failures.
Pro Tip: Bookmark your registrar’s support portal for immediate access to documentation. Most platforms offer live chat for urgent configuration issues.
Conclusion
Configuring web address transitions requires precision to maintain your site’s performance. This guide outlined how permanent path forwarding preserves SEO value while directing users to active content. From selecting the right redirect type to adjusting DNS records, each step ensures seamless domain migrations.
Follow the process: understand URL routing principles, configure your domain settings, and apply troubleshooting checks. Most changes activate within 30 minutes, though global updates may take longer. Proper setup prevents broken links and safeguards your search rankings.
If challenges arise, review the examples and best practices provided. Test configurations thoroughly before finalizing, and monitor traffic shifts post-implementation. For complex scenarios or unresolved issues, consult your platform’s documentation or contact their technical team.
A well-executed strategy keeps visitors engaged and search engines informed. Prioritize accuracy in destination URLs and record management to avoid disruptions. Your efforts today will secure your site’s authority and user trust for years to come.